این مقاله علمی پژوهشی (ISI) به زبان انگلیسی از نشریه الزویر مربوط به سال ۲۰۲۳ دارای ۴ صفحه انگلیسی با فرمت PDF می باشد در ادامه این صفحه لینک دانلود رایگان مقاله انگلیسی و بخشی از ترجمه فارسی مقاله موجود می باشد.
کد محصول: H913
سال نشر: ۲۰۲۳
نام ناشر (پایگاه داده): الزویر
نام مجله: Economics Letters
نوع مقاله: (Short communication)
متغیر : ندارد
فرضیه: ندارد
مدل مفهومی: ندارد
پرسشنامه : ندارد
تعداد صفحه انگلیسی: ۴ صفحه PDF
عنوان کامل فارسی:
مقاله انگلیسی ۲۰۲۳: ترازنامه بانک مرکزی، پول و تورم
عنوان کامل انگلیسی:
Central bank balance sheet, money and inflation
برای دانلود رایگان مقاله انگلیسی بر روی دکمه ذیل کلیک نمایید
وضعیت ترجمه: این مقاله تاکنون ترجمه نشده برای سفارش ترجمه تخصصی مقاله بر روی دکمه ذیل کلیک نمایید (کد مقاله:H913)
مقالات مرتبط با این موضوع: برای مشاهده سایر مقالات مرتبط با این موضوع (با ترجمه و بدون ترجمه) بر روی دکمه ذیل کلیک نمایید
چکیده فارسی
انبساط قوی ترازنامه بانک های مرکزی در واکنش به بحران های اقتصادی از مسیرهای تورمی متفاوتی دنبال شده است. این مقاله نشان می دهد که آیا این انبساط های پولی به افزایش چشمگیر تورم که تابعی از انبساط پولی گسترده است،منجر می شود یا خیر، که بستگی به این دارد که آیا بخش خصوصی، به عنوان واسطه بانک مرکزی برای تامین مالی دولت،بخشی از فرآیند خلق پول بوده است یا خیر. تورم را می توان با آنالیز تعادلی مبتنی بر نظریه مقداری پول توضیح داد. این تحلیل توضیح می دهد که چرا تورم پس از سیاست تسهیل مقداری در ایالات متحده پس از بحران مالی جهانی پایین ماند، اما پس از همه گیری کووید-۱۹ به طور مداوم و چشمگیری افزایش یافته است.
کلیدواژگان: ترازنامه بانک مرکزی، تورم، انباشت پولی، سیاست تسهیل مقداری ( فراخسازی ورود پول )
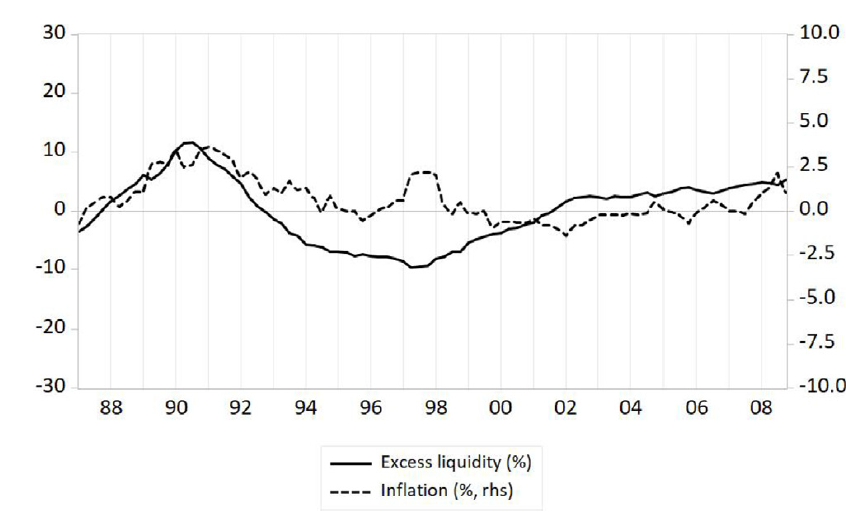
شکل ۴. نقدینگی مازاد و تورم – ژاپن.
Abstract
Strong central banks’ balance sheet expansions in response to economic crises have been followed by different inflation paths. This paper shows that whether or not those expansions resulted in a substantial increase in inflation is function of the associated broad money expansion, which depends on whether the private sector was part of the money creation process as an intermediary to the central bank financing the government. Inflation can be explained by an equilibrium analysis based on the quantity theory of money. This analysis explains why inflation remained low after quantitative easing in the US following the global financial crisis, but has substantially and persistently increased after the Covid-19 pandemic.
Keywords: Central bank balance sheet, Inflation, Monetary aggregates, Quantitative easing
۱.Introduction
Central banks have increasingly been relying on quantitative measures for monetary policy. Balance sheet expansions have however been followed by drastically different inflation outcomes. For example, inflation remained low after quantitative easing (QE) in the US following the global financial crisis (GFC), but substantially and persistently increased after QE following the Covid-19 pandemic. This paper explains those different outcomes with the equilibrium analysis based on the quantity theory of money presented in Reynard (2007), which characterized a systematic empirical relationship between money and inflation in the US and Europe from the 1960s until the 2000s. It focuses on large central banks’ balance sheet expansions in response to economic crises…
۶.Conclusion
The equilibrium approach used in this paper, based on the quantity theory of money, provides a consistent explanation on the effects of central banks’ balance sheet expansions on inflation across historical episodes. The expansions that led to substantial increases in inflation occurred when the central bank explicitly or implicitly, through the private sector, financed the government.
| مقالات مرتبط با این موضوع |
|
مقاله انگلیسی در مورد تورم با ترجمه مقاله isi درباره سیاست های پولی مقاله isi در مورد نظام بانکی با ترجمه |
 پارس پروژه پرتال خدمات دانشگاهی
پارس پروژه پرتال خدمات دانشگاهی